Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair (TEVAR)
This is a procedure designed for qualifying patients at risk of aneurysm rupture or advanced vessel damage. TEVAR is both a safe and reliable intervention performed by our team at BEVSA. The procedure is a minimally invasive option allowing safe repair for patients who are not suitable for open surgery.
Who is eligible for TEVAR?
The aorta is the largest blood vessel in the body, responsible for transporting oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body. The thoracic aorta is the portion of the vessel which begins after the aortic arctic arch and continues down through the thorax (chest), stopping right before the abdomen.
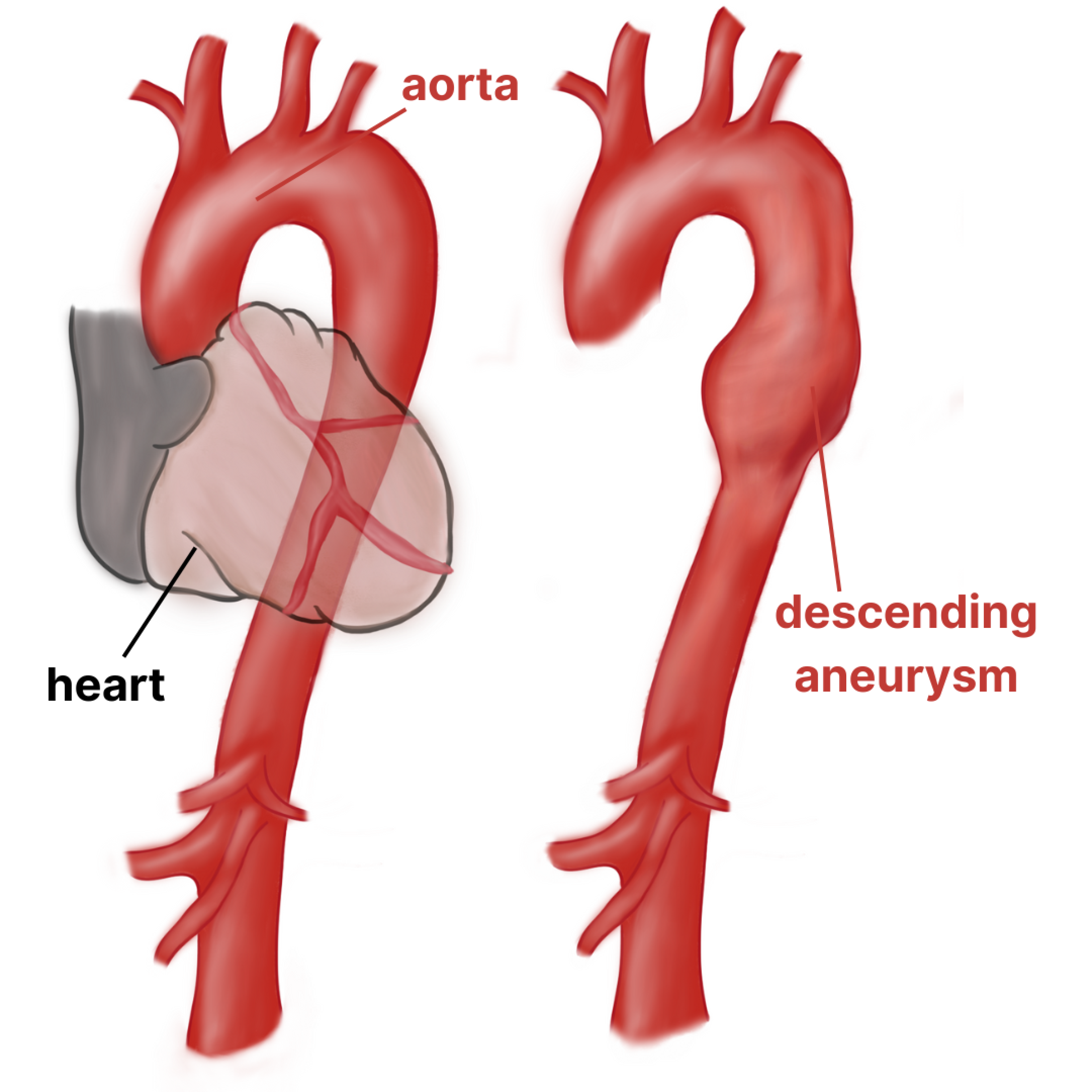
An aneurysm is a bulging or ballooning of the blood vessel when there is an increase in pressure against a weakened portion of the artery wall. Aging and certain risk factors make the descending thoracic aorta a common spot for aneurysm and dissection development.
If left unmonitored and/or untreated, a thoracic aortic aneurysm may grow large enough to rupture–anything larger than 5 cm. Such a rupture is a serious medical emergency causing significant internal bleeding and possibly death.
For patients with an unruptured thoracic aortic aneurysm, your vascular surgeon will assess your aneurysm imaging studies like a CT scan to determine the location and size of your aneurysm. Your vascular surgeon will utilize these findings, as well as your age and comorbidities, to determine the risk of rupture of the aneurysm and if the patient is a suitable candidate for an TEVAR. For patients who need to undergo aneurysm repair, our surgeons will use the minimally invasive TEVAR option where possible due to its lower procedure time and less risk of complications when compared to the traditional open surgical option.
Procedure Details
The TEVAR procedure takes about 2-4 hours at Gates Vascular Institute and most patients are put under general anesthesia, causing the patient to sleep during the procedure.
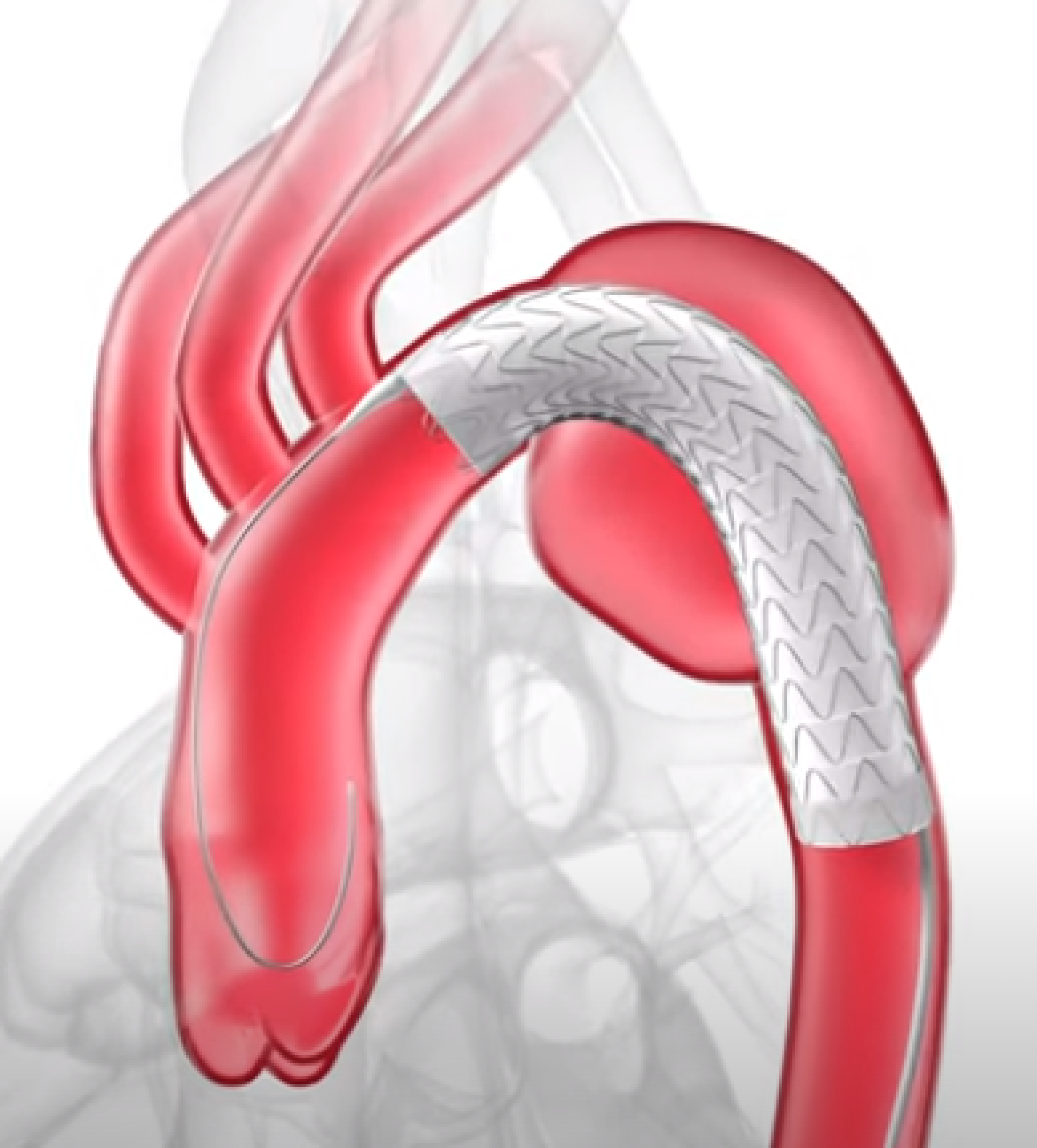
The procedure begins with a small puncture in the patient’s groin to get the sheath into the arteries and up into the aorta. A delivery catheter (a long tube) is placed through the minimally invasive puncture site and guided up the leg via the femoral artery to the thoracic aneurysm.
Throughout the procedure, the vascular surgeon uses real-time x-ray images and contrast dye injections to visualize the aneurysm, catheter, and endograft without having to make a large incision.
The delivery catheter is then positioned to bring the endograft over the site of the aneurysm. The endograft directs blood through the graft itself and prevents blood from flowing into the aneurysm and potentially causing a rupture.
Lastly, your surgeon will inject contrast dye through the endograft system to assess the patients blood flow to ensure proper functioning of the endograft.
Patients, at a minimum, will spend 1-2 nights in the hospital, and most are discharged and able to walk immediately, return home the next day, and go back to work within a week.
Take a look at the video below to see what endograft placement looks like!
What are the potential benefits and risks associated with thoracic endovascular aneurysm repair (TEVAR)?
TEVAR is a new, minimally invasive treatment option that requires a smaller incision, shorter surgery duration, less risk of surgical complication, and shorter recovery time when compared to open repair.
Drawbacks of this procedure are a higher rate of graft complications and possible additional minimally invasive graft repair surgeries when compared to open repair.
Will I feel any different after the procedure?
For the majority of patients, the procedure is a preventative measure meant to reduce the risk of patients developing symptoms and possibly aneurysm rupture. Therefore, most patients report being back to their usual activity in a week or two after the procedure.
Do I need to follow up with my vascular surgeon after aneurysm surgery?
After your aneurysm repair, it is critical to follow up with your surgeon so they can examine your incision sites and check to ensure your graft is placed correctly and functioning well. After your first check-up appointment, your physician will likely want to see you every 6-12 months with CT scans or ultrasound studies to measure the size of your aneurysm and ensure it is not growing. Sometimes, if a leak is discovered in the graft, an additional minimally invasive procedure may be necessary to lessen the risk of aneurysm rupture. Patients who fail to follow up with routine appointments are at an increased risk of aneurysm rupture since we cannot identify and treat any potential problems early on.
Conditions Treatable with Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair (TEVAR)
Descending Thoracic Aneurysms
- Aneurysm
- Aorta
- Thoracic Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (TEVAR)